Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series FunctionsE^x times 1 f' (x)= e^ x this proves that the derivative (general slope formula) of f (x)= e^x is e^x, which is the function itself In other words, for every point on the graph of f (x)=e^x, the slope of the tangent is equal to the yvalue of tangent point So if y= 2, slope will be 2 if y= , slopeMathe^{(xy)}=x^{y}\\/math taking natural log on both sidesmath\\/math math\ln(e^{(xy)})=\ln(x^{y})\\/math math(xy)\ln e=y\ln x\\/math mathsince
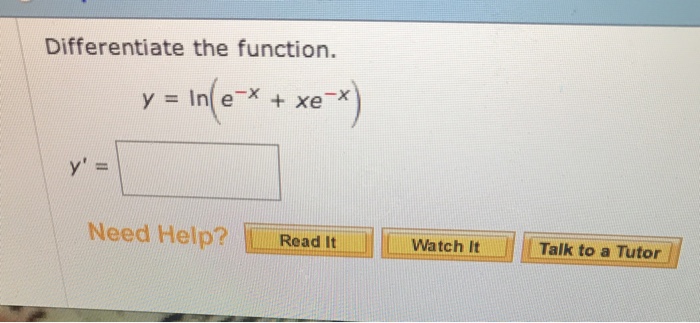
Differentiate The Function Y Ln E X Xe X Y Chegg Com
